[CH] ClickHouse Materialized View
Views
- Normal View
- 資料不會被保存在 disk 中,而是從原本的 table 中直接拿出來
- Parameterized View
- 資料保存方式和 Normal View 一樣,但可以自己定義參數來呈現出不同的資料內容
- Materialized View
- 會建立一個 destination table 來將資料保存在磁碟
- View 中的內容會在 source table 有新資料 Insert 時(UPDATE 或 DELETE 都不會觸發),觸發 MV 中的 SQL,然後寫入 destination table 中。
Regular View
在 ClickHouse 中,一樣可以建立 regular view:
CREATE VIEW uk_terraced_property
AS SELECT *
FROM uk_price_paid
WHERE type = 'terraced';
上面的寫法等同於在 FROM 後面用 subquery:
SELECT count(1)
FROM
(
SELECT *
FROM uk_price_paid
WHERE type = 'terraced'
);
在 ClickHouse 中,一般的 View 並不會保存額外的資料,它只是把 query 保存下來,在每次讀取改 view 時去執行這個 query。
A normal view is nothing more than a saved query.
除非是以下情況比較適合使用一般 view 外,其他的都建議用 Materialized View:
- view 的結果經常會改變
- 即使 view 改變了,它的結果並不會被經常使用
- query 並不是 resource-intensive 的
Parameterized Views
在 ClickHouse 中,可以把參數帶入 Regular View 中,讓這個 view 可以根據不同的參數得到不同的結果。例如:
CREATE VIEW properties_by_town_view
AS SELECT *
FROM uk_price_paid
WHERE town = {town_filter:String};
這時候就多了一個名為 town_name 的參數,可以用來作為 town 這個欄位的 filter:
-- town_name 變成可以帶入的參數
SELECT COUNT()
FROM properties_by_town_view(town_filter = 'LONDON');
Materialized Views (MV)
Using Materialized Views in ClickHouse @ ClickHouse > Blog
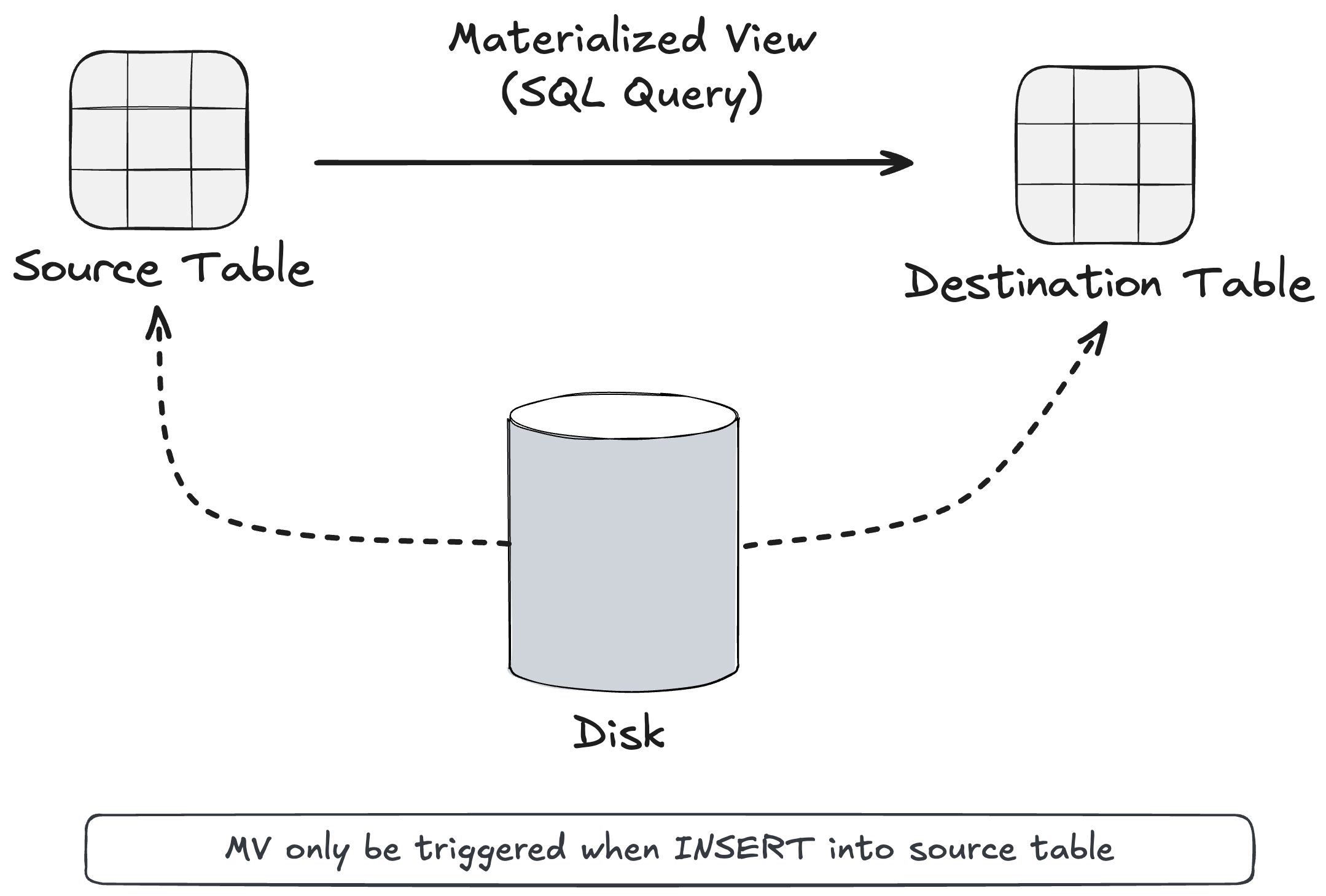
基本說明
-
Materialized Views 實際上只是一個 pipeline,把 source table 的資料透過 MV 這個 pipeline 保存在另一張 destination table
- MV 中所寫的 SQL 會在 source table 有新資料被 INSERT 時執行,執行後的結果則會保存到 destination table 中。也就是說,MV 比較像是 source table 到 destination table 的一個 pipeline。
- 每一個 MV 預設背後都會有一個 hidden table 被建立,這個 table 被稱作 destination table。比較好的做法是手動先建立出 destination table ,接著再建立 MV 時,透過
TO來把 source_table 的資料塞進 destination table
-
當有新的資料寫進 source_table(triggered table)時,同樣的資料會經過特定的 Query 後也寫進 Materialized View
- MV 絕對不會直接去讀原本的 source table
-
因為只有 INSERT 會觸發 MV 更新,所以��如果你的操作會用到 UPDATE 或 DELETE,那 MV 可能不適合你使用,PROJECTION 可能會比較適合
只有 INSERT 會觸發 MV,如果是 DELETE 或 UPDATE 的操作都不會對 MV 產生作用。也就是說,如果會有 UPDATE 或 DELETE 操作的需求,MV 可能不是合適的方法。
-- 先建立 MV
-- 這裡使用 ENGINE = MergeTree 而不是用下面會提到的 TO,因此 ClickHouse 會自動建立一個 hidden table 來保存這個 View 的資料
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW uk_prices_by_town
ENGINE = MergeTree
ORDER BY town AS
SELECT
price,
date,
street,
town,
district
FROM uk_price_paid;
-- 接著再把原本已經存在的資料 INSERT 到 MV
INSERT INTO uk_prices_by_town
SELECT
price,
date,
street,
town,
district
FROM uk_price_paid;
uk_price_paid被稱作 source table 或 triggered table,一旦有新的資料 insert 到uk_price_paid,則這個新的資料會經過同樣的 querySELECT price, date, ...這個 query,然後進到uk_prices_by_town這個 MV。
需要特別留意的是,每次有新 INSERT 的資料時,這些新的資料會經過同樣的 query,但原本就存在 destination table 中的資料則不會被再次拿出來重算,也就是說,如果 SELECT 裡有用到 avg、max、等 aggregate function 的話,計算出來的結果並不會考慮原本就存在 destination table 中的資料,而是會完全根據該次 INSERT 的資料所算出的 avg 或 max,多數�的時候這並不會是我們預期的結果。
要解決這個問題的方法會需要使用到下個段落提到的 AggregatingMergeTree。
建立 MV 的 Best Practice
前面提到,只有新 INSERT 到 source table(trigger table)的資料會進到 MV 中,因此如果要建立 MV 又不想讓 source table 還有 MV 中看到的資料不一致,可以跟著下面這三個步驟:
- 定義並建立 destination table
- 在建立 MV 時,使用 TO 來指定 destination table
- 把 source table 中的資料,重新倒進 destination table 中
STEP 1:定義並建立 destination table
CREATE TABLE uk_prices_by_town_dest
(
`price` UInt32,
`date` Date,
`street` LowCardinality(String),
`town` LowCardinality(String),
`district` LowCardinality(String)
)
ENGINE = MergeTree
ORDER BY town;
STEP 2:在建立 MV 時,使用 TO 來指定 destination table
前面提到,在建立 MV 時,ClickHouse 實際上會先建立一個 .inner_id.{uuid} 的資料表,這個資料表被稱作 destination table。為了避免資料庫中有太多這種 .innerXXX 資料表,比較好的方式是手動先把 destination table 建立出來,接著在建立 MV 時,透過 TO 來指定要把資料保存到這個 destination table 中。
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW uk_prices_by_town_view
TO uk_prices_by_town_dest
AS SELECT
price,
date,
street,
town,
district
FROM uk_price_paid
WHERE date >= toDate('2024-02-19 12:30:00')
- 使用 TO 來指定要存到那個 destination table,這裡是前一步建立好的
uk_prices_by_town_dest - 這裡的
WHERE會指定一個快到的時間點,例如 5 分鐘後,這會讓這個 table 在指定的時間才開始有資料能新增進來,目的是要讓我們的資料有一個清楚的切結點,知道哪個時間點以前的資料要自己手動新增到 destination table 中。舉例來說,假設現在是2024-02-19 12:25:00,五分鐘後是2024-02-19 12:30:00,因此要在這個時間點之後才會有資料新增到這個 destination table,透過這樣的方式,我們可以清楚知道12:30:00以前的資料,需要再自己 INSERT 到 destination table 中。
這裡使用 WHERE 指定未來的時間點只是其中一種做法,只要能讓新舊資料有一個清楚的切分點的做法都可行。例如,也可以這裡不要用 WHERE,等 MV 收到資料後,找出最早進來的資料的時間點,即��表示資料都要在這個時間後才會自動進到 MV 中,因此在這個時間點以前的資料,就需要自己從 source table INSERT 到 destination table 中。
使用 POPULATE 可以在建立 MV 時,直接把 source table 中原本就存在的資料也新增到 MV 中,但因為 POPULATE 的過程需要時間,特別是資料量大時,這可能會使得在這段時間內 trigger table 收到的資料,不會被加入到 MV 中,進而導致兩邊的資料有落差。
STEP 3:把 source table 中的資料,重新倒進 destination table 中
一旦資料有了清楚的切分點,最後一步就是把原本存在 source table 但不存在 destination table 的資料 INSERT 到 destination table 中:
把資料從 source table 倒回 destination table 的方式就和執行 MV 中的 SQL 是一樣的。
INSERT INTO uk_prices_by_town_dest SELECT
price,
date,
street,
town,
district
FROM uk_price_paid
WHERE date < toDate('2024-02-19 12:30:00');
AggregatingMergeTree
- AggregatingMergeTree @ SQL Reference > Engines > Table Engines > MergeTree Family
- Using Aggregate Combinators in ClickHouse @ ClickHouse Blog
假設我們有一個需要經常被重複 query 到的資料,例如 avg(price),雖然這個計算在 ClickHouse 非常快,但它卻很重複。如果我們可以確保「舊的資料不會被更新」的話,那麼我們就可以保存一個「running average」,只有在有新的 row 被 INSERT 時,才更新這個計算出來的平均數。
STEP 1:建立 AggregatingMergeTree Table (destination table)
在 destination table 中,除了 Primary 的欄位之外,其他 column 的資料型別只會是 AggregateFunction 或 SimpleAggregateFunction 這兩種 Data Type,它們實際上是保存 aggregation 的狀態(state)
CREATE TABLE uk_aggregated_prices
(
`district` String,
`avg_price` AggregateFunction(avg, UInt32),
`max_price` SimpleAggregateFunction(max, Float32),
`quant90` AggregateFunction(quantiles(0.9), UInt32)
)
ENGINE = AggregatingMergeTree
PRIMARY KEY district;
The columns in an AggregatingMergeTree table that are not in the sort key need to be of type AggregateFunctionor SimpleAggregateFunction.
AggregatingMergeTree collapses rows with the same sort order into a single row, not with the same PRIMARY KEY.
STEP 2:使用 -State 來建立 Materialized View
- 這個 Materialized View 會在
uk_price_paid這個 source table 有新的資料進來時,執行對應的 SQL 後寫進uk_aggregated_prices這個 destination table - 在 Materialized Table 中,需要使用
-State/-SimpleStatecombinators 來保存 aggregating 的中介狀態(intermediate states)
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW uk_aggregated_prices_view TO uk_aggregated_prices
AS SELECT
district,
avgState(price) AS avg_price,
maxSimpleState(price) AS max_price,
quantilesState(0.9)(price) AS quant90
FROM uk_price_paid
GROUP BY district;
STEP 3:把 source table 中的資料,重新倒進 destination table 中
把資料從 source table 倒回 destination table 的方式就和執行 MV 中的 SQL 是一樣的:
INSERT INTO uk_aggregated_prices
SELECT
district,
avgState(price) AS avg_price,
maxSimpleState(price) AS max_price,
quantilesState(0.9)(price) AS quant90
FROM uk_price_paid
GROUP BY district;
STEP 4:使用 -Merge functions 來檢視 aggregating 的資料結果
在 Select 的時候,對於 AggregateFunction data type 的欄位,需要使用 -Merge combinators 才能把所有保存的「中介狀態」合併起來,以獲得最終的結果:
SELECT
district,
avgMerge(avg_price),
max(max_price),
quantilesMerge(0.9)(quant90)
FROM uk_aggregated_prices
GROUP BY district
LIMIT 5;
Parts merge whenever they merge - you have no control over it. This means you can easily have multiple rows with the same sort key that have not collapsed into a single row yet.
When querying the columns of an AggregatingMergeTree table, you should always GROUP BY the sort key and use the appropriate -Merge function, in case there are multiple rows in the table with the same sort key that have not collapsed yet into a single row.
SummingMergeTree
SummingMergeTree 會自動把相同 Sorting Key 的 rows 做合併,並且將 Numeric Data Type 的 Column 做合併,如此可以提升效能並節省許多儲存空間。然而,因為無法確定這個合併什麼時候會發生,所以在 Query 的時候一定要搭配 sum 和 GROUP BY 使用。
STEP 1:建立 destination table
CREATE TABLE prices_sum_dest
(
town LowCardinality(String),
sum_price UInt64
)
ENGINE = SummingMergeTree()
ORDER BY town;
STEP 2:建立 Materialized View
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW prices_sum_view
TO prices_sum_dest
AS
SELECT
town,
sum(price) AS sum_price
FROM uk_price_paid
GROUP BY town;
STEP 3:把資料從 Source Table 倒進 Destination Table
把資料從 source table 倒回 destination table 的方式就和執行 MV 中的 SQL 是一樣的:
INSERT INTO prices_sum_dest
SELECT
town,
sum(price) AS sum_price
FROM uk_price_paid
GROUP BY town;
STEP 4:檢視 Destination Table 的資料
由於 SummingMergeTree 沒有保證什麼時候會將資料做合併,所以務必要搭配 sum 和 GROUP BY 以確保得到正確的結果:
SELECT
town,
sum(sum_price) AS total_price,
formatReadableQuantity(total_price)
FROM prices_sum_dest
GROUP BY town
ORDER BY total_price DESC
LIMIT 10;